Use medical terminology and abbreviations related to pharmacology.
Use medical terminology and abbreviations related to pharmacology.
In this final assessment in this course, remember that you are assuming an office manager role in a family practice office. Your office offers monthly 30-minute educational sessions for patients on a variety of topics. You have been given the opportunity to present at next month\\\’s session. In Assessment 3, your faculty member approved your topic and provided you with feedback on it. Since then you have been using credible resources to research your health topic. For this final assessment, you are to prepare your slide presentation with speaker notes for your educational session. You will also submit an audio recording and transcript of your presentation.DEMONSTRATION OF PROFICIENCYBy successfully completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
Competency 1: Use medical terminology and abbreviations related to pharmacology.
Apply medical terminology related to pharmacology or other treatments to a health topic.
Competency 2: Use medical terminology and abbreviations related to general structures and functions of the human body.
Apply medical terminology related to the structure and functions of the human body to a health topic.
Competency 3: Use medical terminology and abbreviations related to body systems.
Apply medical terminology related to human body systems to a health topic.
Competency 4: Use medical terminology and abbreviations related to specialized areas of medicine.
Apply medical terminology related to a specialized area of medicine, including diagnostic or surgical procedures, to a health topic.
Competency 5: Analyze and define medical terminology as used in health information management.
Apply medical terminology used in health information management.
Competency 6: Spell and pronounce basic medical terms.
Pronounce medical terms properly.
Spell medical terms correctly.
Competency 7: Communicate in a professional manner.
Create a presentation that is clearly written, organized, and generally free of grammatical errors.
Provide title and reference slides that conform to APA style and format.
Use volume, tone, and clarity reflective of professional communication in a health care setting.
Click Health Topic Presentation | Transcript to view a media piece that provides a brief example of a presentation.
Complete your research on the health topic of your presentation. Consult the HIM-FPX4610: Medical Terminology Library Guide for research tips and help in identifying credible resources.
Consult the Capella Writing Center as needed for additional writing resources to help you develop your presentation.
Set up and test your microphone or headset using the installation instructions provided by the manufacturer. You only need to use the headset if your audio is not clear and high quality when captured by the microphone.
Practice using the equipment to ensure the audio quality is sufficient.
Microsoft PowerPoint allows you to record your narration with your slides. If you choose to record your presentation using this tool, simply submit your presentation to the appropriate area of the courseroom. Your narration will be included with your slides.
Consult the Using Kaltura [PDF] for guidance in how to record your presentation and upload it in the courseroom if you elect not to use Microsoft PowerPoint to submit your slides and narration.
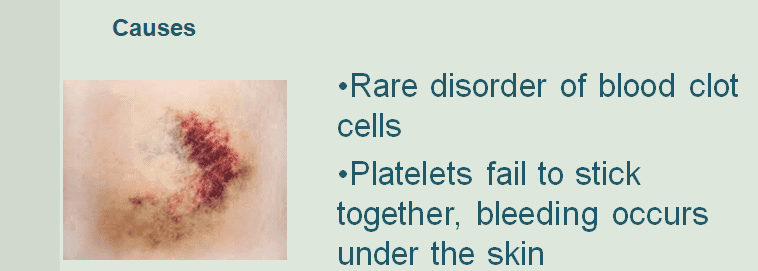
Causes.
Signs and symptoms.
At risk population(s).
Prognosis.
Diagnostic or surgical procedures.
Treatment protocols, including pharmacology treatments.
Support systems.
Prevention.
Your 10 to 15 slides with speaker notes, including title and reference slides in APA format.
Your audio recording of your presentation.
A transcript of your presentation.
Writing: Your presentation does not need to conform to APA style and formatting guidelines. It does need to be clear, well organized and generally free of grammatical errors. You do need to provide title and reference slides that conform to APA style and format.
Length: Your presentation is not to exceed 30 minutes in length.
Scoring Guide: Be sure to read this assessment\\\’s scoring guide, so you understand how your faculty member will evaluate your work.
SCORING GUIDEUse the scoring guide to understand how your assessment will be evaluated.VIEW SCORING GUIDE
HEALTH TOPIC PRESENTATION
The topic of this presentation is ITP, and it includes the:
- definition (including analysis and pronunciation);
- description;
- etiology;
- signs and symptoms;
- who is at risk and prognosis;
- diagnostic testing and procedures;
- treatment protocols;
- support systems;
- prevention; and
- references.
The definition of ITP is that it is a medical abbreviation for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Here is an analysis of the terms in that definition: Idiopathic means pertaining to an unknown disease. Begin with the suffix, -ic, which means pertaining to. Then progress to combining the forms: path/o, which means disease, and idi/o, which is defined as unknown. Thrombocytopenic means that it pertains to a deficiency of clotting cells. Begin with the suffix, -ic, which means pertaining to, and the suffix -penia, which means deficiency. Then progress to the term thrombocytes, which means clotting cells. Purpura means bleeding into the skin. It\\\’s a Latin term that means purple color. So when you put it all together, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is pertaining to an unknown disease process of deficient clotting cells, characterized by purplish spots on the skin.
ITP, or idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, is also known as immune thrombocytopenic purpura. ITP is a rare disorder of blood clotting cells. Thrombocytes, also known as platelets, do not stick together to clot, so bleeding under the skin and within the body can occur. The etiology of ITP is not known. Some sources, such as the NIH (2012), have indicated that ITP might be linked to bacterial or viral infections in some people.
Signs are things that can be seen, such as bleeding under the skin or in the mouth (gums); petechiae (red spots as depicted here), nosebleeds, and blood in urine or stool. Symptoms are things that are felt, such as depression and fatigue.
Who is at risk for ITP? In children, ITP may occur at any age. It is usually acute. It sometimes develops after a viral infection. It is not contagious, and the prognosis for children is usually recovery within one year. In adults, ITP may occur at any age. It is usually chronic. Women are two to three times more likely than men to have ITP. It is not contagious. The prognosis for ITP in adults is that it may result in an intracranial hemorrhage and even death, although this is rare.
Diagnostic protocols may include a physical examination, blood tests to check platelet count, and a blood smear to look at platelets. If the blood tests show a low platelet count, bone marrow tests may follow.
Pharmacological treatment for ITP may include corticosteroids administered intravenously to help increase platelet count. Other treatments may include Rituximab, immune globulin, anti-Rh immunoglobulin, and herbal medications. A splenectomy, which is a surgical excision to remove the spleen, may be required to reduce proteins produced by the spleen that destroy platelets in individuals with ITP. Platelet transfusions may also be necessary.
A few support systems for people with ITP and their families include the following: The ITP Foundation is a support system for helping children and adolescents live with ITP. Their web site is itpfoundation.org. PDSA is the Platelet Disorder Support Association for people with ITP. Their web site is pdsa.org. The site also lists additional treatment protocols for ITP.
Although no known prevention exists for ITP because the etiology of ITP is unknown, a healthy lifestyle helps prevent diseases. Early detection is important. People should have an annual physical exam with blood tests for platelet counts. They should also know the signs and symptoms, and when to see a doctor. This concludes the presentation on ITP.
REFERENCES
- Cambridge Dictionary. (2017). Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Retrieved from http://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/pronunciation/english/immune-thrombocytopenic-purpura
- Cancer Care of Western New York. (2017). Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Retrieved from https://www.cancercarewny.com/content.aspx?chunkiid=96582
- Chabner, D-E. (2017). The language of medicine, 11th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier.
- ITP Foundation. (2017). Retrieved from http://www.itpfoundation.org/
- Merriam-Webster. (2017). Retrieved from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/purpura
- National Institute of Health: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2012). Immune thrombocytopenia. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/itp
- PDSA. (2017). Treatments. Retrieved from https://www.pdsa.org/about-itp/early-detectionprevention.html
CREDITS
Subject Matter Expert:
Earla White, PhD, RHIA
Interactive Design:
Marty Elmer, Marc Ashmore
Instructional Designer:
Carmen Garland
Project Manager:
Andrea Thompson
Health Topic Presentation Scoring Guide
CRITERIANON-PERFORMANCEBASICPROFICIENTDISTINGUISHEDApply medical terminology related to pharmacology or other treatments to a health topic.
Does not apply medical terminology related to pharmacology or other treatments to a health topic.
Applies medical terminology related to pharmacology or other treatments to a health topic; however, omissions and/or errors exist.
Applies medical terminology related to pharmacology or other treatments to a health topic.
Applies medical terminology related to pharmacology or other treatments to a health topic and provides supporting examples and specifics.
Apply medical terminology related to the structure and functions of the human body to a health topic.
Does not apply medical terminology related to the structure and functions of the human body to a health topic.
Attempts to apply medical terminology related to the structure and functions of the human body to a health topic; however, omissions and/or errors exist.
Applies medical terminology related to the structure and functions of the human body to a health topic.
Applies medical terminology related to the structure and functions of the human body to a health topic and provides supporting examples and specifics.
Apply medical terminology related to human body systems to a health topic.
Does not apply medical terminology related to human body systems to a health topic.
Attempts to apply medical terminology related to human body systems to a health topic; however, omissions and/or errors exist.
Applies medical terminology related to human body systems to a health topic.
Applies medical terminology related to human body systems to a health topic and provides supporting examples and specifics.
Apply medical terminology related to a specialized area of medicine, including diagnostic or surgical procedures, to a health topic.
Does not apply medical terminology related to a specialized area of medicine, including diagnostic or surgical procedures, to a health topic.
Attempts to apply medical terminology related to a specialized area of medicine, including diagnostic or surgical procedures, to a health topic; however, omissions and/or errors exist.
Applies medical terminology related to a specialized area of medicine, including diagnostic or surgical procedures, to a health topic.
Applies medical terminology related to a specialized area of medicine, including diagnostic or surgical procedures, to a health topic and provides supporting examples and specifics.
Apply medical terminology used in health information management.
Does not apply medical terminology used in health information management.
Attempts to apply medical terminology used in health information management; however, omissions and/or errors exist.
Applies medical terminology used in health information management.
Applies medical terminology used in health information management to a health topic and provides supporting examples and specifics.
Spell medical terms terms correctly.
Does not spell medical terms correctly.
Attempts to spell medical terms correctly, however, errors exist.
Spells most medical terms correctly.
Spells all medical terms without any errors.
Pronounce medical terms properly.
Does not pronounce medical terms properly.
Attempts to pronounce medical terms properly; however, errors exist.
Pronounces most medical terms properly.
Pronounces all medical terms properly without any errors.
Create a presentation that is clearly written, organized, and generally free of grammatical errors.
Does not create a presentation that is clearly written, organized, and generally free of grammatical errors.
Attempts to create a clearly written, organized, and grammatically correct presentation; however, omissions and/or errors exist.
Creates a presentation that is clearly written, organized, and generally free of grammatical errors.
Creates a presentation that is clearly written, organized, and free of grammatical errors, and provides supporting examples and specifics.
Provide title and reference slides that conform to APA style and format.
Does not provide APA title and reference slides that conform to APA style and format.
Attempts to provide title and reference slides that conform to APA style and format; however, omissions and/or errors exist.
Provides title and reference slides that conform to APA style and format.
Provides title and reference slides that conform to APA style and format, without any errors.
Use volume, tone, and clarity reflective of professional communication in a health care setting.
Does not use volume, tone, and clarity reflective of professional communication in a health care setting.
Attempts to use volume, tone, and clarity reflective of professional communication in a health care setting, but lapses and/or errors exist.
Uses volume, tone, and clarity reflective of professional communication in a health care setting.
Uses volume, tone, and clarity reflective of professional communication in a health care setting consistently, without lapses or errors.
Answer preview to use medical terminology and abbreviations related to pharmacology.
 14 slides
14 slides
Get instant access to the full solution from yourhomeworksolutions by clicking the purchase button below
The post Use medical terminology and abbreviations related to pharmacology. appeared first on Yourhomeworksolutions.
-
- Assignment status: Resolved by our Writing Team
Comments
Post a Comment